| 1888 |
 Chronomedia index Chronomedia index
Numbers after entries link to the list of references. |
links and notes |
| January 10 |
Le Prince is granted a US patent (no 376247) for a 16-lens motion picture camera and projector. |
> October |
| April 24 |
Eastman Kodak Company is founded by George Eastman (1854-1932). Within a year he perfects and markets the first affordable camera using roll film. |
|
| May 3 |
Kodak name is registered in the UK. |
cf September 4 |
| May 16 |
Flat gramophone disc is demonstrated by Emile Berliner to members of the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia. His technique involves coating a zinc disc with a wax resist into which the stylus cuts the recording. The disc is then etched in acid to cut the recording into the zinc. Berliner intends to use the electrotyping process to make copies of the zinc master disc and demonstrates a copper duplicate. |
|
| June 16 |
 Allegedly after five solid days and nights of work, Edison and his associates complete a prototype of an improved phonograph. Like the Bell and Tainter graphophone, it now has an electric motor and uses wax cylinders. The event is commemorated in one of the most famous photographs associated with invention. Allegedly after five solid days and nights of work, Edison and his associates complete a prototype of an improved phonograph. Like the Bell and Tainter graphophone, it now has an electric motor and uses wax cylinders. The event is commemorated in one of the most famous photographs associated with invention. |
|
| June 29 |
Edison's foreign sales agent, Colonel George Gouraud, makes a cylinder recording in the Crystal Palace, London of a 4,000-strong choir performing Handel's Israel in Egypt at a distance of more than 100 yards from the phonograph. |
Until 2008 this is the oldest known music recording. |
| July 14 |
North American Phonograph Company is founded by Jesse Lippincott to market phonographs and graphophones. The company sells regional franchises to lease equipment, sharing the $40 annual rental per machine with the franchisee. Lippincott, a Pittsburgh businessman, who has just made $1m from the sale of his controlling stake in the Rochester Tumbler Company, spends $200,000 to become sole licensee of the American Graphophone Company, which continues to make players that Lippincott markets. Shortly after, Lippincott spends $500,000 on acquiring Edison’s patents in the phonograph, although Edison retains manufacturing rights. This gives Lippincott control of the entire US cylinder sound recording business. However, Lippincott shares Edison’s view of the invention as a dictating machine. Columbia Phonograph Company, which services the District of Columbia, Delaware and Maryland area, is one of 30 licensees. |
|
| August |
First photography on film by John Carbutt in the USA, using Kodak equipment invented by George Eastman. |
|
| September 4 |
Kodak name is registered in the USA. |
cf May 3 |
| |
Edison meets Muybridge and becomes interested in developing a visual recording machine similar to the Zoöpraxiscope. |
|
| October 17 |
Edison files a caveat at the US Patent Office for an optical phonograph, with images only 1/32 inch wide. Edison's claim is that it will 'do for the eye what the phonograph does for the ear'. |
|
| October |
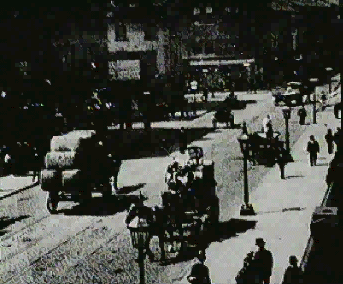 Le Prince shoots experimental film footage in Leeds, England, on paper strips 54mm wide and projected using a Maltese cross mechanism. Le Prince shoots experimental film footage in Leeds, England, on paper strips 54mm wide and projected using a Maltese cross mechanism. |
Some of these films can be viewed on and downloaded from the website of the National Museum of Photography, Film and Television [Click on picture for link]. |
| • |
Charles-Emile Reynaud devises and demonstrates the Théâtre Optique projection device, also known as Pantomimes lumineuses. Animated images are projected from long celluloid strips of hand-drawn coloured images, with perforations for registration purposes. |
> 1893 |
| • |
Edison attempts to raise capital for phonograph development from New York investment bank J & W Seligman & Company but failure of the working model to work leads nowhere. |
> 1926 December 7 |
| • |
 Wordsworth Donnisthorpe and W C Crofts make a film camera that takes pictures in a circular frame. Wordsworth Donnisthorpe and W C Crofts make a film camera that takes pictures in a circular frame. |
> 1891 |
| |
Electric motor, using AC power, is invented by Nikola Tesla (1856-1943) in US. |
|
| • |
Pianist Josef Hofmann, aged 12, visits Edison’s laboratories and makes some phonograph cylinder recordings—the first by a recognised performer. Soon after, celebrated conductor Hans von Bülow faints when he hears the playback of a Chopin mazurka he has just recorded. |
A Punch cartoon satirises this idea. |
| • |
Wilhelm Hallwachs develops Heinrich Hertz's work on the photoelectric effect, observing that when illuminated with ultraviolet light, a negative charged, well-insulated body loses its charge. |
|
| |
Heinrich Hertz demonstrates the practical possibility of radio transmission. |
|