









 |
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1928 | Numbers after entries link to the list of references. |
links and notes |
| Cultural highlights | Predictions made this year | ||
| January 1 | In the Netherlands, Algemeene Vereeniging Radio Omroep (AVRO) begins broadcasting. | |
| January 2 | First religious Daily Service is broadcast by BBC radio; 50 years later it has an audience of 500,000 a day and is still running. | |
| January 17 | A M Josepho patents a fully automated photographic film processing device. | |
| January | F W Murnau uses a primitive camera crane on the production of The Four Devils for Fox in Hollywood. It is nicknamed 'the go-devil'. | |
| • | Gaumont British controls 187 cinemas—by far the largest British circuit—through the consolidation of Denman Picture Houses and General Theatre Corporation. | > 1929 February |
| February 9 | John Logie Baird transmits television pictures across the Atlantic by landline from Motograph House, London to Bert Clapp's station GK2Z at 40 Warwick Road, Coulsdon, Surrey, thence by radio transmission to his business colleague Captain Hutchinson at Hartsdale, NY. | |
| February 18 | French government issues a decree, effective from 1 March 1928, giving the Ministère de l'Instruction Publique control over film distribution and censorship. Powers are available to require foreign producers to acquire French productions in exchange for their films being released in France. All censorship is to be carried out by the ministry but with local police override provisions. Any producer of an 'anti-French' film could have all his films banned in France. An import quota requiring US distributors to take one French film for distribution in the US for every four US films released in France is imposed. | |
| February 25 | Charles Jenkins Laboratories in Washington DC is granted the first Federal Radio Commission licence for an experimental television station. | |
| February | Warner Bros goes into production with the first all-talking picture, The Lights of New York. | |
| February | Statutes for the International Educational Cinematographic Institute (IECI) are drawn up in Rome. [0038] | > August |
| March 1 | With the new French cinema decree now in force, the Ministère de l'Instruction Publique delays censoring all American films, causing a shortage of product for exhibition in French cinemas. [0041] | |
| March 12 | BBC Dance Orchestra, led by Jack Payne, makes its first broadcast. |
|
| March 27 | Radio station KGB begins transmissions in San Diego, California. | |
| March | First Soviet Five-Year Plan is applied to the film industry, progressively eliminating imports and using export revenue to build the production industry. Manufacturing of raw film stock is to begin—the country being wholly dependent on imports—but Western sound technology is not to be adopted. | |
| March-May |  Instructions for building a Baird Televisor are published in the first two issues of Television, the'official organ' of the Television Society. The third issue, in May [left], gives details of how to send television pictures between two rooms. Instructions for building a Baird Televisor are published in the first two issues of Television, the'official organ' of the Television Society. The third issue, in May [left], gives details of how to send television pictures between two rooms.The complete instructions are reproduced on this website courtesy of the Royal Television Society. |
 Build your own Baird Televisor. |
| April 20 |
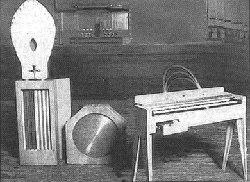 Maurice Martenot gives the first public performance of his electronic 'ether-wave' musical instrument, the Ondes Martenot [right], at the Paris Opéra, performing Poème symphonique by the Greek composer Dimitrios Levidis. Maurice Martenot gives the first public performance of his electronic 'ether-wave' musical instrument, the Ondes Martenot [right], at the Paris Opéra, performing Poème symphonique by the Greek composer Dimitrios Levidis. |
|
| April 25 | Chancellor of the Exchequer Winston Churchill makes the first Budget broadcast on the BBC. | |
| April | Report by the Royal Commission into monopoly practices in the Australian film industry is presented to parliament. The outcome is a clause in distribution/exhibition contracts allowing a five per cent rejection of American films to allow Australian films in, two cash prizes (for best Australian scenario and production) and a two-year hiatus in Australian production, pending the outcome of the report. However, the number of films produced in Australia this year is the highest for a decade. | Films > 1929 Prizes > 1930 |
| April | [Photo: Terra Media Archives] |
|
| April | Gainsborough Pictures formed in UK by Michael Balcon and C M Woolf. Later in the year it is acquired by Gaumont-British. | |
| spring | Internationale Tentoonstellung op Filmgebied is held in The Hague, Netherlands—an international film exhibition that also includes Soviet participation for the first time since the Russian Revolution. [0038] | |
| May 2 | Radio station KPQ begins transmissions in Wenatchee, Washington, USA. | |
| May 4 | France's cinema decree is modified to change the import quota: 60 per cent of US films imported in 1927 are retrospectively excluded and licences are granted to import seven foreign films for every French production. The decree is to be renegotiated after one year. The import allowance is not reached. [0041] | |
| May 11 | First regular scheduled television transmissions begin from General Electric Company’s WGY Schenectady, NY station. The low-definition system broadcasts half an hour on three days a week—Tuesday, Thursday and Friday. | |
| May 11 | Hollywood studios' committee formally adopts Western Electric sound-on-film audio system, which ERPI would manufacture and lease exclusively to US cinemas. | |
| • | Western Electric charges $11,300 to install variable density sound-on-film audio systems in cinemas with fewer than 1,000 seats, $15,300 for cinemas with 1,000-1,750 seats and $19,000 for larger auditoria. RCA charges range from $8,500 to $17,000 for its variable area system. [0025] | |
| May | All major Hollywood studios adopt Western Electric’s sound-on-film system, rejecting Warner Bros’ Vitaphone sound-on-disc format, also developed by Western Electric, a subsidiary of General Electric, in turn part of AT&T, which has a patent arrangement with Lee De Forest, on whose amplification system of vacuum tubes the system depends. Cross-licensing agreements are reached with RCA and Westinghouse to produce two sound-on-film formats, both compatible in projectors. RCA markets Photophone and another AT&T subsidiary, Electrical Research Products, controls Westrex. AT&T continues to support Vitaphone for three or four years to come. Estimates of the cost of converting studios to sound production vary between $23m and $50m. | |
| • |  To compete with Western Electric’s in-roads into the new sound-on-film market, Radio-Keith-Orpheum (RKO) is formed by the merger of three film companies—one each in production, distribution and exhibition (brought together by Joseph P Kennedy, the politician and father of the future president, who made $5m on the deals)—and Radio Corporation of America (RCA). David Sarnoff becomes chairman of RKO, which becomes one of the top five Hollywood producers within a couple of years. To compete with Western Electric’s in-roads into the new sound-on-film market, Radio-Keith-Orpheum (RKO) is formed by the merger of three film companies—one each in production, distribution and exhibition (brought together by Joseph P Kennedy, the politician and father of the future president, who made $5m on the deals)—and Radio Corporation of America (RCA). David Sarnoff becomes chairman of RKO, which becomes one of the top five Hollywood producers within a couple of years. |
|
| • | RCA begins work on large-screen television. | > 1930 January |
| June 8 | General Electric's WGY television station starts broadcasting two half-hour programmes three days a week at 13:30 and 23:30. | |
| June 12 | First outdoor television transmission is made by Baird on his roof in 133 Long Acre, London, featuring actor Jack Buchanan. | |
| June | Baird International Television Ltd, formed with £700,000 capital, is heavily over-subscribed. | |
| June | Short-wave radio telephony is introduced between London and New York. | |
| July 2 | Federal Radio Commission grants the first television broadcasting licence (W3XK) to Jenkins Television Corporation of Maryland. Charles F Jenkins' mechanical scanning system is used. The station's limited bandwidth (10 kH) means that only silhouettes can be transmitted to provide signals for experimenters building their own receivers. | |
| July 3 | Baird demonstrates a colour television system using sequential scanning through red, green and blue filters. | |
| July 6 | First all-talking motion picture, Lights of New York, is premiered in New York. | |
| July 16 | Paramount decides that all releases for the coming year with be sound-on-disc, even if the film also has a soundtrack. Projectionists are instructed to insert a mask in the projector to blank off the soundtrack, resulting in an aspect ratio of approximately 1.13:1 instead of the usual 1.33:1. | |
| July 30 | Kodacolor, based on patents acquired by Eastman Kodak in 1925, is introduced. | |
| July 31 | MGM's first talking picture release, White Shadows on the South Seas, is prefaced with the growl of Leo, the MGM trademark. | |
| July | Daven Corporation of Newark, NJ advertises the first commercially produced and available television receiver, adjustable for 24-, 36- or 48-line transmissions, and priced at $75. | |
| July | Rights are granted in the UK for wireless transmission of still pictures by the Fultograph system. Invented by Otto Fulton of Wireless Pictures Ltd, the receiver has a 4ins x 5ins screen and costs £22. The experiment survives until November 1929. | |
| August 10 | Baird demonstrates television pictures with a stereoscopic relief effect. | |
| August | Baird announces that his transmitter at 133 Long Acre, nearing completion, will be used for his own programmes, in response to the BBC’s demand for higher quality. | |
| August | Statutes of the International Educational Cinematographic Institute are approved by the Council of the League of Nations. Italy will provide annual funding of 600,000 lire. [0038] | > November 5 |
| September 11 | General Electric’s station WGY at Schenectady, NY broadcasts the first television play, The Queen’s Messenger by J Hartley Manners. | > 1937 January 19 |
| September 19 |  First talking cartoon film, Walt Disney’s Steamboat Willie, is premiered at the Colony Theatre, New York, introducing Mickey
Mouse. Plane Crazy, another Mickey Mouse talkie completed earlier, is released later. First talking cartoon film, Walt Disney’s Steamboat Willie, is premiered at the Colony Theatre, New York, introducing Mickey
Mouse. Plane Crazy, another Mickey Mouse talkie completed earlier, is released later. |
|
| September 19 | Radio station KOH begins transmissions in Reno, Nevada. | |
| September | Warner Bros acquires a majority interest in First National Pictures. | |
| September | The Jazz Singer opens at the Piccadilly Theatre, London. | |
| September 28-October 6 | Attracted by a thriving radio music scene and using mobile recording equipment, producer Ralph Peer of Victor Talking Machine Company makes the first recordings in Nashville, Tennessee: 69 songs by nine acts, mostly of country music. | |
| October 9 | Baird demonstrates his television system to BBC officials, who react unfavourably. | |
| October 9 | Radio Manufacturers Association (RMA— later the Electronic Industries Association, EIA) forms a television committee to consider a framework for the introduction of television. | |
| October 18 | Kodacolor, a three-colour additive lenticular process developed by Eastman Kodak (see also July), is demonstrated to the Royal Photographic Society, London. | |
| October 30 | Start of a year's experimental transmissions of still pictures from the BBC's Daventry transmitter using the Fultograph system. | |
| November 5 | International Educational Cinematographic Institute (IECI) is opened in Rome by King Victor Emmanuel. The director is Luciano de Feo, former director of Istituto LUCE; de Feo says, 'We hope ... to secure ... an effective system of co-operation with the great cinema industry in researches designed to bring about a constant improvement in the type of film produced.' | |
| November 11 | Several US radio stations begins transmissions: KXO in El Centro, California; WGH in Newport News, Virginia; WGL in Fort Wayne, Indiana; WMT in Cedar Rapids, Iowa; WOL in Washington DC. | |
| early December | Warner Bros' Vitaphone Company releases its first sound film in a foreign language: Zweiundvierzigste Strasse (42nd Street), an eight-minute comedy that is shown in German-speaking areas of the US. | |
| November 13 | Vladimir Zworykin is granted a patent for a colour television imaging tube in which the screen is composed of a mosaic of squares in the three primary colours. | < 1925 |
| November 20 | Radio station WGL in Fort Wayne, Indiana begins transmissions. | |
| November 22 | The talkie The Home Towners opens at the Piccadilly Cinema, Denman Street, London. | |
| November | Associated British Cinemas (ABC) registered with £1m capital, taking control of British International Pictures, Scottish Cinema and Variety Theatres chains. It starts with a chain of 40 cinemas. | > 1930 |
| November | By now, no Loews theatre in New York has an orchestra or organist. No longer needed in sound-equipped cinemas, organists move into radio. | |
| November | Coverage of the enthronement of Emperor Hirohito is the first nationwide Japanese radio broadcast. | |
| December 4 | Announcement is amde at a Television Society meeting that members could 'test their apparatus at midnight when the first of a series of experimental test programmes would be put on the ether for one hour by the Baird Company'. | |
| December 6 | Canadian government appoints a Royal Commission ‘to examine into the broadcasting situation in the Dominion of Canada and to make recommendations to the Government as to the future administration, management, control and financing thereof’. Chairman is Sir John Aird, President of the Canadian Bank of Commerce. | |
| December 17 | London Section of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers holds is inaugural meeting. | |
| Another talkie, On Trial, written by Elmer Rice, opens at the Piccadilly Cinema, Denman Street, London. | ||
| December 25 |  Premiere of first talking western, In Old Arizona, at Fox West Coast Criterion Theater, Los Angeles. Shot on location in Utah and California. |
|
| • | Of 294 feature films released by the seven major Hollywood studios 220 are silent, 10 are all-talking—all made by Warner Bros—and 23 are part-talkie; the other 41 have sound effects and/or music but no dialogue. | Hollywood shifts from silent to sound |
| • | Of 520 feature films released in the US during the year, about 200 are imported. [Source: FIlm Daily Year Book.] | |
| • | In Germany two major sound film companies are founded: Ton-Bild Syndikat (Tobis), funded by Swiss and Dutch venture capital with only a minority German stake, owns the Tri-Ergon patents; Klangfilm has backing from AEG and Siemens. | |
| • | During the year 48 sound stages are built in Los Angeles. [0025] | |
| • | ERPI installs sound film equipment in 879 US cinemas during the year, bringing the total at year end to 1,046. [0025] | |
| • | During the year a total of $161.93m is spent on building and equipping new cinemas in the USA. [0058] | |
| • | Boston station WLEX uses film in occasional telecasts. | |
| • | Paramount buys the Katz-Balaban cinema circuit, which is merged with other exhibition interests to form the Publix Corporation. [0058] | |
| • | Paramount buys into CBS radio with a view to develop cross-media programming. | |
| • | American film companies set up British production subsidiaries or fund local producers to make cheap British films (‘quota quickies’) to accompany their releases and thus qualify under the Cinematograph Films Act. Fox Film Company sets Fox-British Pictures. | |
| • | First UK purpose-built sound-proof studio for talking pictures is built at Ealing, London by Associated Talking Pictures. Joint managing director is producer Basil Dean. [0019] | |
| • | Ludwig Blattner buys the former Neptune Studios at Elstree for his British Phototone Sound Productions (aka Ludwig Blattner Film Corporation). Despite Blattner’s technical competence, initially the studios are silent, although neighbouring Elstree studios are equipped for sound. [0019] | |
| • | Julius Hagen and Henry Edwards of Neo-Art with film director Leslie Hiscott, form Twickenham Films Studios Limited. [0019] | |
| • | British Instructional Films (Proprietors) is registered in UK as a company and starts to build a studio at Welwyn, Hertfordshire. Novelist John Buchan is on the board. [0019] | |
| • | Worton Hall Studios at Isleworth is sold to British Screen Productions. [0019] | |
| • | By now Soviet films are producing more box office revenue in the USSR than imports. [0036] | |
| • | RCA Photophone sound system is installed at Islington Studios, London. [0019] | |
| • | First feature-length film made in Greece: To Limani ton Dacrion (The Port of Tears), directed by Dimitrios Gaziadis. | > 1930 |
| • | First Budget broadcast, explaining the policies, is made on BBC radio by Winston Churchill, Chancellor of the Exchequer. | |
| • | British interests in international cable and wireless telegraphy and telephony are merged into a single company, called Imperial & International Communications, later Cable & Wireless. | |
| • | Cost of transatlantic telephone calls on the single channel between London and New York is reduced to £9.00 for the first three minutes. | |
| • | Vladimir Zworykin uses film for television transmission tests at RCA labs. | |
| • | Television experiments are demonstrated in Japan by Kenjiro Takayanagi of Hamamatsu Technical High School at a 'television conference' of the Tokyo branch of the Electrical Academy in Kanda. | > 1931 |
| • | Eastman Kodak introduces Eastman Type 2 panchromatic motion picture film, which is sensitive to all colours in the spectrum. It also increases the speed of its standard fine-grain panchromatic negative film from 20 ASA to 40 ASA. | |
| • | Al Jolson's recording of Sonny Boy and There's a Rainbow Round My Shoulder from his second talkie, The Singing Fool, sells 2m disc copies; Sonny Boy also sells a million copies in sheet music form. | |
| • | Bubble gum is invented by Walter Diemer (1904-1998), an accountant at the Fleer Chewing Gum Company, Philadelphia. 'It was an accident,' he says in 1996. |
Page updated 6 March 2009
© David Fisher